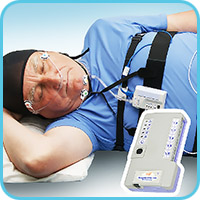
Sleep signals recorder "ApnOx"
Medicom MTD. Medical equipment for electrodiagnosis, rehabilitation and research
Phones: +7 (8634) 62-62-42, 62-62-43, 62-62-44, 62-62-45.
www.medicom-mtd.com
Polysomnographs of different types for sleep disorders diagnostics
Polysomnography is a "gold standard" of sleep disorders diagnosis.
The International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD) describes the different types of sleep disorders, such as obstructive or central sleep apnea syndrome, snoring, Cheyne-Stokes respiration, restless legs syndrome (RLS), bruxism, insomnia, hypersomnolence, parasomnias, and more than 90 types of other sleep disorders (www.sleepnet.ru).
Chronic sleep disorders can cause:
- cardiac pathologies, such as arterial hypertension, arrhythmia, congestive heart failure (CHF);
- metabolic changes, hormonal regulation, and, as a result, obesity, diabetes, and other diseases;
- neurological and psychosomatic disorders, such as epilepsy, chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency, dysregulation of excitation and inhibition, depression, anxiety.
AASM classification defines different types of polysomnographs:
- Systems recording a small number of parameters (Type III) with function of data recording onto a memory card in autonomous mode. Type III systems have a limited number of channels (from 4 to 15) and are used primarily for advanced respiratory (sleep apnea screening) and cardiorespiratory monitoring in a hospital, health and sleep research centers, or at home.
- Mobile polysomnographic system (Type II) differ from Type III systems in number of channel (from 18 to 24) and include up to 6 EEG channels for sleep stages analysis and hypnogram building. The study can be performed in autonomous mode without a technician.
- Stationary polysomnographic systems (Type I) include 24 and more channels. A characteristic feature of Type I systems is an increased number of EEG channels to diagnose sleep disorders related to epilepsy and other neurological diseases. System can include extra channels for ECG, EMG, motor activity, and other parameters (GSR, PPG, temperature, wetness, etc.).
- Each type of polysomnographs can be supplemented with mobile or stationary kit for synchronized overnight video monitoring. The polysomnographs can control the performance of CPAP therapy as well.
Type IV AASM
"ApnOx-04"
for respiartory screening вҖ“ 3 channels
Signals and parameters:
- oxygen saturation (SpO2);
- photoplethysmogram, pulse rate, perfusion index, respiratory rate and conventional respiratory amplitude (based on SpO2);
- pressure airflow;
- snore and airflow velocity (based on the airflow data);
- body position and total movement activity (integrated accelerometer sensor);
- CPAP Pressure.
Recording modes:
- autonomous вҖ“ data recording onto memory card;
- telemetric вҖ“ data transmission into computer via wireless Bluetooth® channel.
Type III AASM
"ApnOx-10"
for cardiorespiratopry monitoring вҖ“ 7 and more channels
Includes all the components of ApnOx-04 modification and wireless module Poly-4
Records the entire set of ApnOx-04 parameters, as well as:
- thoracic and abdominal respiratory effort;
- electrocardiogram (ECG);
- heart rate (based on ECG);
- pulse wave transit time (based on ECG and PPG);
- snore (accelerometer sensor);
- airflow (thermistor airflow sensor);
- motility;
- skin conductance;
- signals from DC-inputs.
For detailed information, please go to the website apnox.com
Type II/I AASM
Electroencephalograph-recorder "Encephalan-EEGR-19/26", modification "Mini"
(AT-Somno (Type II), AT-Somno-Video (Type I) versions)
with "Encephalan-PSG" software for somnological studies
A system with an increased number of channels (18-24), including up to 6 EEG channels, provides telemetric and autonomous record of physiological signals using autonomous patient transceiver-recorder ABP-10, wireless pulse oximeter module, other modules, electrodes and sensors. This system provides the same functionality for cardiorespiratory disorders analysis as the polysomnograph based on sleep signals recorder "ApnOx-10" (type III).
"Encephalan-PSG" software ("Maximum" suite) displays brain rhythms power indices, EOG and EMG amplitude, parameters of respiration, movements, snoring and ECG in a form of trends for quick search of EEG patterns, identification of sleep stages, as well as for manual and automatic hypnogram building, and anlysis of various sleep disorders.
"Encephalan-PSG" software provides automatic calculation of such additional sleep statistical parameters by EEG as:
- total sleep time;
- sleep stages duration;
- sleep efficiency;
- sleep latencies and stages latencies;
- number, indices and duration of EEG arousals;
- number and duration of awakenings (WASO).
Type II/I AASM
Electroencephalograph-recorder "Encephalan-EEGR-19/26", main modification
(AT-PSG (Type II), AT-PSG-Video (Type I), AT-PSG-Video-Poly (Type I) versions)
with "Encephalan-PSG" software for somnological studies
Polysomnographs of type I are characterized by an increased number of EEG channels (20 and more) to diagnose sleep related forms of epilepsy and other neurological diseases.
The polysomnographs are suitable both for stationary application in expert class sleep laboratories and for mobile application.
The sales package includes autonomous patient transceiver-recorder ABP-26, wireless pulse oximeter module, other modules, electrodes, and sensors.
Polysomnograph's software additionally provides analysis of multichannel sleep EEG, detection of epileptic patterns and classification of spike-waves in relation to sleep structure using various methods of EEG quantitative analysis.
Kits of video equipment with "Encephalan-Video" software provide visual analysis of paroxysmal activity and symptoms of sleep disorders synchronously with electrical brain activity that is crucial in differential diagnosis of epilepsy.
|
Phones: |
Frunze str., 68, Taganrog, |
| © 1997-2024 Medicom MTD Ltd All rights reserved | |

 Brochure
Brochure Video
Video
 Illustrated catalogues
Illustrated catalogues Apnox-04 report
Apnox-04 report